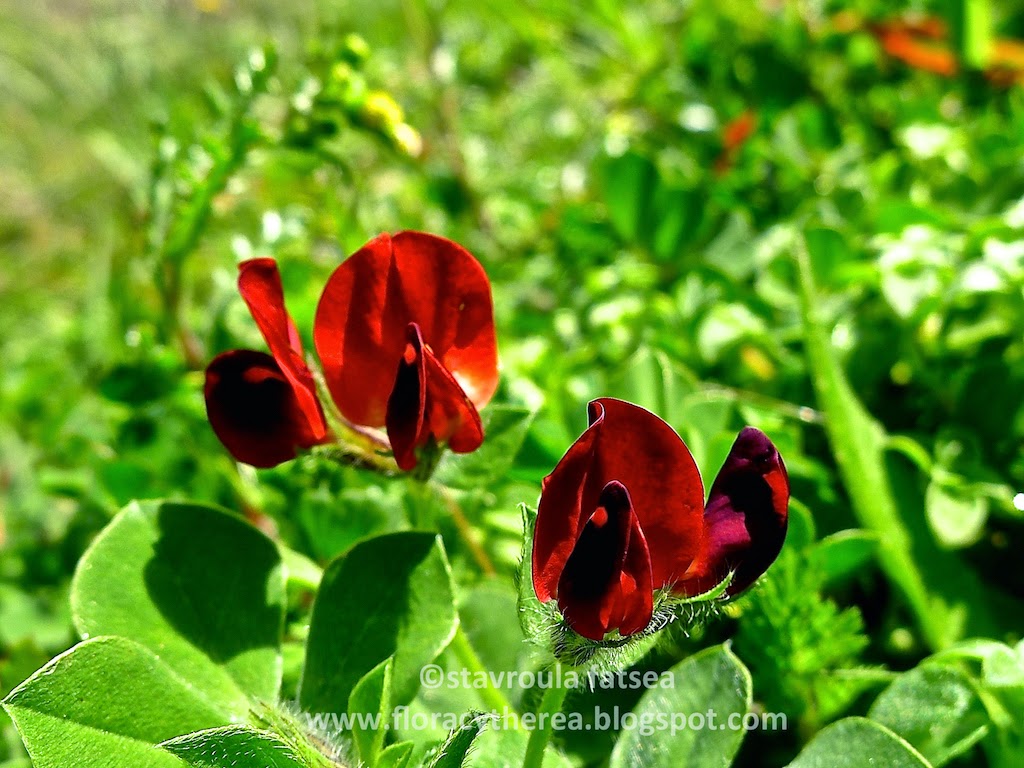
Syn. Tetragonolobus palaestinus Boiss.&Blanche
Lotus tetragonolobus L.
An annual plant, native to the Mediterranean, North Africa, and the Middle East. It has spread as an epigeic plant in China, Australia, and Northern Europe. It loves sunny locations and grows in cultivated or uncultivated fields and on roadsides. It is cultivated as a fodder plant. It is believed to restore nitrogen levels in the soil.
The roasted seeds are used as a substitute for coffee. The tender pods are eaten raw or cooked in salads, soups, and oil-based dishes. Their taste is reminiscent of asparagus, hence one of their common names in English: asparagus pea.
Its leaves have astringent and healing properties.
In Crete, it is called aspago or santalida, while the common name mantalo is also known in Kythira, especially in the southern part of the island.
The scientific name comes from the Greek word τετράγωνο + λωβός, referring to the characteristic shape of its lobes. Its adjective comes from the Latin purpureus – a -um = purple.