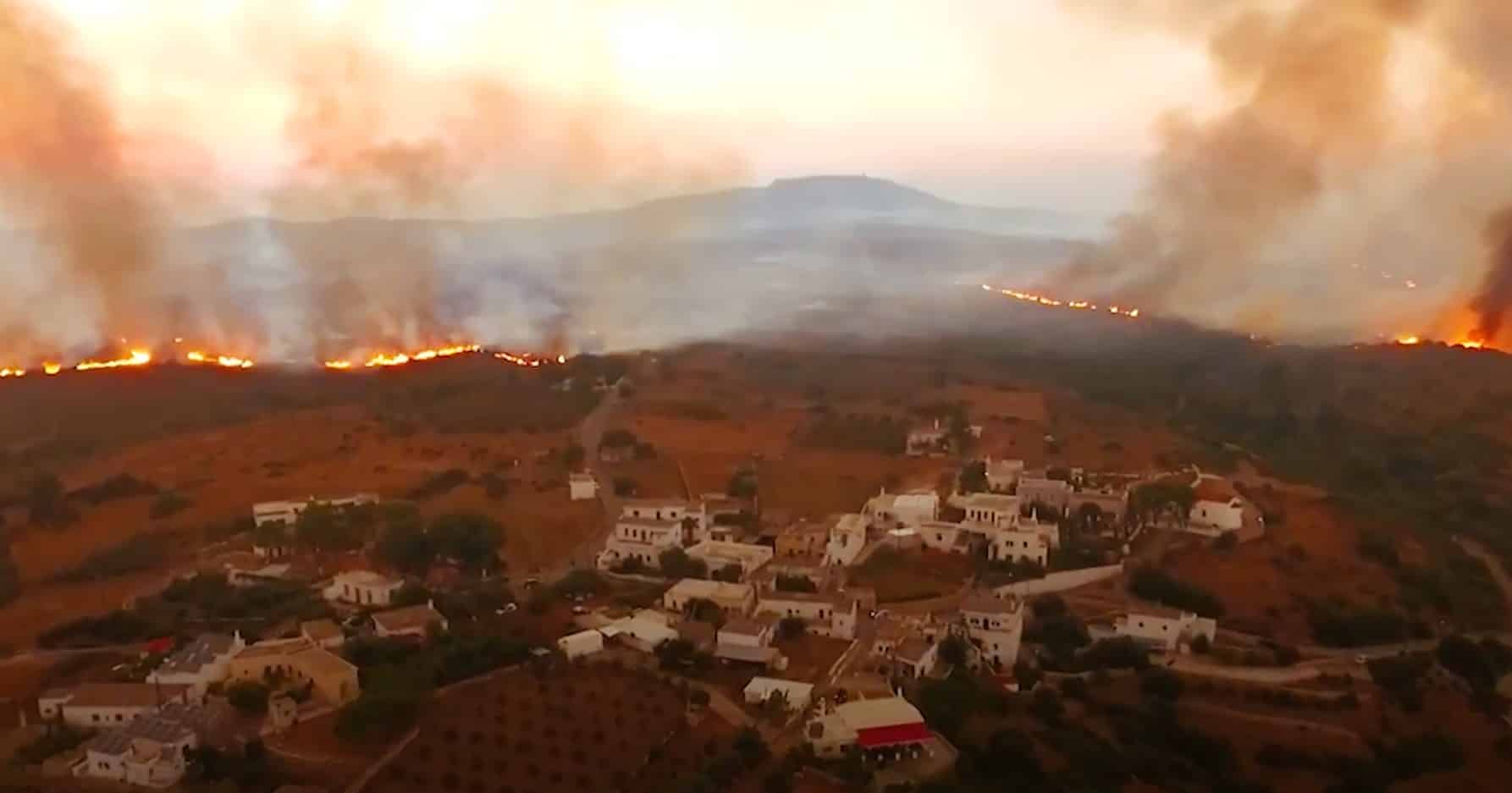
The smoke from the extensive fires in our country has worsened atmospheric conditions even in remote areas, such as Antikythera, as shown by a study conducted by the ReaCT team at the Institute of Astronomy, Astrophysics, Space Applications & Remote Sensing (IAASARS) of the National Observatory of Athens (NOA).
According to the records of the PAGGAIA Observatory of the National Observatory of Athens in Antikythera, the load of suspended smoke particles in the atmospheric column is six times greater than the average observed in August.
Furthermore, as shown by measurements taken by the Institute, which are part of the NASA-AERONET network, smoke layers are transported to distant areas at altitudes of up to 3 km, affecting atmospheric conditions at distances as far as Africa.